Introduction
Humans are afraid of several things, which is normal. But when fears transgress into a state of anxiety disorder in which a person has an intense, illogical dread of a living being, place, object or situation, it becomes a phobia. So phobias of any kind can be distressing in the long term. They cause a lot of stress, anxiety, and panic. The phobia of animals is known as zoophobia.
Our Wellness Programs
What is Zoophobia?
Zoophobia is the phobia of animals. A zoophobic person experiences extreme disgust and fear of animal(s).
However, want to know some amazing facts about this phobia? So keep reading until the end for ten zoophobia facts you probably didn’t realise until now.
Looking for services related to this subject? Get in touch with these experts today!!
Experts

Kirti Bajpai

India
Psychologist
Experience: 5 years

Neelam Parwani

India
Life Coach
Experience: 5 years

Mansi Chawla

India
Psychologist
Experience: 12 years
How to Identify Zoophobia?
Zoophobia is an uncontrollable fear of being around animals. So it is an anxiety disorder that causes significant distress to people who experience it.
An individual suffering from zoophobia may show the following symptoms:
- Feeling intense fear, anxiety and stress when in close vicinity or thinking about an animal they are scared of or one invokes a response in them.
- There is an imbalance and inability to function when faced with the trigger of being around that animal.
- Uncontrollable fear of specific animals.
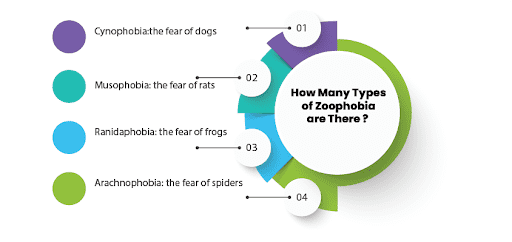
How many types of Zoophobia are there?
So there are several types of zoophobia. The most common ones include:
- Cynophobia: the fear of dogs
- Musophobia: the fear of rats
- Ophidiophobia: the fear of snakes
- Ichthyophobia: the fear of fish
- Ranidaphobia: the fear of frogs
- Herpetophobia: the fear of reptiles
- Chiroptophobia: the fear of bats
- Ailurophobia: the fear of cats
- Ornithophobia: the fear of birds
- Arachnophobia: the fear of spiders
What are the effects of Zoophobia?
So the effects of zoophobia include psychological symptoms such as:
- A strong sense of fear
- Panic
- Stress
- Anxiety
Now physical symptoms include:
- A rapid increase in heart rate
- Tingling
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Confusion
- Vomiting
- Sweating
- Chills and fever
- Intense sweating
Children may often become numb, scream or hide to avoid the trigger source at all costs.
What is the reason behind zoophobia?
Experts have not been able to pinpoint the cause of zoophobia accurately yet. Nevertheless, certain factors can predispose a person to the same. They could range from genetics to family members passing on the fear and individual trauma.
Here is a breakdown of some of the causes:
-
Negative experience
Negative experiences with an animal in the past or a traumatic situation where one may have to face an animal can explain zoophobia. These incidents profoundly impact a person’s mind, leading to phobia formation.
-
Genetic predisposition
However genetic predisposition is another reason behind zoophobia. It means one may inherit genetic information from parents and their characteristics of fearing animals. One may also learn this behaviour as a child they see their parents scared of animals in front of them.
-
Negative thoughts
Now another thing that can cause zoophobia is negative thoughts. However, one may have a thinking pattern where they create irrational fear in their minds about animals and think they only attack them. This irrational fear often creates negative thoughts, and a person may want to avoid that trigger at all costs.
How to overcome zoophobia?
Here are some steps to overcome zoophobia:
-
Take it one day at a time:
One does not wake up one day and get over zoophobia. It has to be taken one day at a time. For instance, small gradual exposure and trying to make yourself comfortable around the feeling are essential.
Now other ways to gradually conquer the fear could include watching the animal’s pictures, imagining them in positive, safe spaces, and engaging in conversations about these animals in a friendly way that does not cause any irrational thinking.
-
Therapy:
Therapy is another way of overcoming zoophobia. Now speaking to a practitioner about your fears, undergoing a different type of behavioural therapy, looking at your situation objectively, and facing the triggers are other ways of meeting zoophobia.
-
Breathe and meditate:
Have a calm mind and objectively face the situation with strength. So breathe and calm yourself down with ease.
What is the treatment for zoophobia?
There are several treatments for zoophobia. Now some of the most commonly used treatments are cognitive behavioural therapy, exposure therapy, and medication control the symptoms:
-
Exposure therapy:
However, exposure therapy is the first line of treatment for zoophobia. So in this treatment, people need to confront their fears. According to therapists’ suggestions, this is in cases where people try to avoid any source of the trigger.
According to exposure therapy, practitioners create a safe environment and gradually expose individuals to the triggers they are trying to avoid. So the kind of exposure therapy differs from case to case. Still, some of the most commonly used exposure therapy is when a therapist or mental health professional asks the person to face a feared animal in a safe environment.
-
Cognitive-behavioural therapy:
Another approach for treating zoophobia is cognitive-behavioural therapy. In this, the person understands irrational thinking, which may be causing significant distress.
They form new realistic thought patterns, which help people let go of the anxiety response they may face. So it also includes cognitive restructuring, systematic exposure, and mindfulness training. It allows people to look away from their thoughts, detach from the situation, and reason.
-
Medication:
Now, therapists also suggest using medicine to treat the intense effects of zoophobia. So, the most commonly used ones are beta-blockers and benzodiazepines.
10 Zoophobia Facts that Will Make you Rethink your Fear of Animals
So, do you know these facts about zoophobia? Have a look below:
- Now spiders and snakes are some of the most common animals that evoke strong responses of fear and disgust.
- However, creatures that cause maximum discomfort in people are tapeworms, louse roundworms, spiders, and snakes.
- So there are two spectrums in Zoophobia. The first type of trigger is usually disgust after seeing an animal, and the second type of response is fear after seeing that animal.
- If we observe, we notice Zoophobia may present in families. So it may pass on to children with family members afraid of animals.
- Untreated zoophobia can worsen with time.
- Zoophobia can increase the chances of developing depression, anxiety, and social isolation disorders.
- However, one can be diagnosed with zoophobia if one meets the criteria of the 5th edition of D.S.M. 5—a manual for the diagnosis of mental health disorders.
- So most people with zoophobia rarely seek treatment because of intense fear and perceptions around zoophobia.
- Zoophobia can begin in childhood and may also be in adulthood.
- The amygdala of the brain often triggers Zoophobia.
Conclusion
However, zoophobia is an intense feeling which causes disgust and fear of animals. So it is not specific to a particular animal, and different people face different types of specific phobias. Now they become anxious and stressed and try to avoid the triggers. The treatment for this phobia includes C.B.T., exposure therapy, and medications. So these treatments can help a person face the fear objectively, and gradually they can live a better quality of life. The trained mental health professionals at United We Care deal with anyone suffering from it or other phobias. Feel free to reach out for more information!
| [1] | Psychiatry.org. [Online]. Available: https://psychiatry.org/psychiatrists/practice/dsm/frequently-asked-questions. [Accessed: 25-Aug-2022]. |
| [2] | “Zoophobia and Entomophobia,” SCIplanet. [Online]. Available: https://www.bibalex.org/SCIplanet/en/Article/Details.aspx?id=13634. [Accessed: 25-Aug-2022]. |
| [3] | M. Zvaríková, P. Prokop, M. Zvarík, Z. Ježová, W. Medina-Jerez, and P. Fedor, “What makes spiders frightening and disgusting to people?,” Front. Ecol. Evol., vol. 9, 2021. |