Introduction
Senior medical professionals often refer to psychiatrists as the “obstetricians of the mind” because they are experts in handling brain disorders. We face little memory and understanding problems as we age, forgetting names and places or taking extra time to understand directions. These problems may become progressive as a routine part of ageing. Some older people also develop severe problems remembering, understanding, or thinking, leading to delirium. Delirium is a mental state often associated with drowsiness, disorientation, and hallucinations.
Our Wellness Programs
What is Delirium?
Delirium is a confused, disoriented state where someone cannot think or remember correctly. It usually appears suddenly. It is frequently transient and curable. Delirium is a mental and emotional illness caused by an imbalance in brain chemistry that occurs suddenly. Delirium can happen when someone is detoxing from alcohol, recovering from surgery, or recovering from dementia. Delirium is usually for a short time and treatable. Delirium is a significant cause of death and disability in hospitalised elderly adults and often signals serious illness in younger patients.
Looking for services related to this subject? Get in touch with these experts today!!
Experts

Banani Das Dhar

India
Wellness Expert
Experience: 7 years
Devika Gupta

India
Wellness Expert
Experience: 4 years

Trupti Rakesh valotia

India
Wellness Expert
Experience: 3 years

Sarvjeet Kumar Yadav

India
Wellness Expert
Experience: 15 years
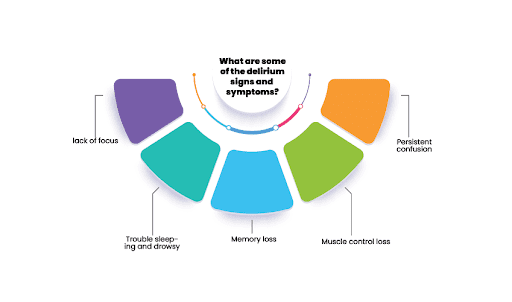
What are some of the delirium signs and symptoms?
Delirium influences your intellect, emotions, motor control, and sleeping habits. You may find it difficult to concentrate on your whereabouts. You may also suffer mood changes and move more slowly or swiftly than average.
Other signs and symptoms could include:
- A lack of capacity to focus
- Trouble sleeping and drowsy
- Memory loss for short-term
- Muscle control loss (as in urinary incontinence)
- Increase in alertness in the morning and a decrease at night
- Persistent confusion
- Disorganised thinking, talking in a way that makes little sense
- Emotional changes: anger, agitation, irritability, overexcitement
- Hallucinations and delusions
If Delirium is significant, people may lose track of who they are or who else is around them. People with incoherence have trouble thinking and ramble, occasionally becoming nonsensical. Some people feel paranoia or delusions (false beliefs). Depending on the intensity and cause, Delirium can linger for hours, days, or weeks.
What are the causes of Delirium?
Many conditions can lead to Delirium if they develop or worsen. Unessential use of medicines that alter brain function might cause them to become delirious (psychoactive drugs).
Many factors cause Delirium, the most prevalent of which are:
- Anticholinergic medicines, psychotropic drugs, and opioids are examples of drugs.
- Severe Dehydration
- Pneumonia, a bloodstream infection (sepsis), infections that affect the entire body or create a fever, and U.T.I.s are all ailments.
- Kidney failure, liver failure, and a low quantity of oxygen in the blood (hypoxia) are all dangerous, especially if they develop abruptly and quickly.
Hospitalisation, surgery, the abrupt discontinuation of a long-term medication, and toxins are other reasons. Delirium can occur in less critical conditions in older people, especially those who suffer from stroke, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, or brain damage from another disorder.
Delirium can also result from less severe conditions such as:
- Minor illnesses (U.T.I. s)
- Intense constipation
- Needless use of a bladder catheter
- A lack of sleep for a prolonged period
What is the treatment for Delirium?
You can observe delirium patients at the emergency clinic for a short time and then send them home. Psychiatrists or other experts follow the following practices.
1. Treatment of the cause
- General measures
- Management of agitation
2 Treatment of the cause
Surgeons often identify the cause of Delirium and promptly correct or treat it. Doctors may treat infections with antibiotics, dehydration with intravenous fluids and electrolytes, and incoherence caused by abstaining from alcohol with benzodiazepines. Treatment of the delirium-causing condition is possible, and it frequently prevents lasting brain damage and leads to a full recovery.
3. General measures
Dehydration, malnutrition, incontinence, falls, and pressure sores are common concerns in Delirium. Preventing such issues necessitates cautious attention.
4. Management of agitation
People who are agitated or experience hallucinations have a higher risk of injuring themselves or their caretakers. Staying with the person’s family is encouraged. The person’s medication routine should be simple. You may want to avoid keeping devices, such as injectable lines and bladder catheters, near a person with delirium since they might further confuse and agitate the patient, increasing the risk of harm.
Many doctors prefer two drugs that control agitation, but neither is ideal.
Antipsychotic medicines are the most commonly prescribed medications. However, they have the potential to prolong or exacerbate agitation. Recent antipsychotic medicines like risperidone and olanzapine have fewer side effects than traditional antipsychotics like haloperidol.
Psychiatrists use benzodiazepines (sedatives) such as lorazepam for Delirium caused by withdrawal from a sedative or alcohol. Because benzodiazepines can make patients, especially the elderly, more confused, sleepy, or both, they are not used to treat Delirium caused by other diseases. Doctors are cautious when providing these medications, especially for the elderly.
How steady do you beat Delirium?
- Doctors can identify people at high risk of Delirium in seniors.
- They can put specific interventions that can go a long way toward avoiding Delirium.
- If Delirium progresses, experts can address and alleviate symptoms by treating the underlying causes and implementing preventative methods.
- Prevention and management strategies may include assisting the seniors family in enabling the elderly to exercise regularly, consume nutritious foods, and healthily drink water.
- Regular yoga and meditation practice can help patients overcome Delirium. It may be a simple, safe, low-cost way to increase brain fitness.
Conclusion
Researchers believe that some changes in brain chemicals cause Delirium. Doctors define Delirium as an abrupt transition in mental status that can cause disorientation, memory problems, or changes in a person’s emotions or state of awareness. It is curable and preventable. It occurs for a brief period, but people should seek medical attention if they exhibit any signs of Delirium. Patients who practise yoga and meditation regularly can beat Delirium. Feel free to reach out to the many mental healthcare professionals at United We Care to learn the differences between depression, dementia, and Delirium. Remember – Once you correctly identify delirium, you can treat it out of your life.

 Conflict Management in Relationships
Conflict Management in Relationships
 Healing from Heartbreak
Healing from Heartbreak Coping With Anxiety
Coping With Anxiety Get Started With Mindfulness
Get Started With Mindfulness Healing With Meditation
Healing With Meditation


