Introduction
Our connection to those we love is something special. This special bond gives us a sense of security, love, and calmness. However, it is largely determined by how we were treated and nurtured by our mom and dad during our childhood – which in turn, shapes our attachment style. There are four attachment styles – secure, anxious, avoidant, and fearful-avoidant. These styles impact how we think and react to our emotions when we are in a romantic relationship as grown-ups.
“All hurt is founded on attachment to anything regardless of its nature. When we detach, we vibrationally send ourselves back into the flow of life.” -Dr. Jacinta Mpalyenkana [1]
Understanding the Attachment Style
We all create relationships that help us emotionally. After expansive research, Psychologists John Bowlby and Mary Ainsworth proposed the Attachment Style Theory in 1958. They suggested that how we were treated in our childhood by our primary caregivers is what determines our relationships as adults [2].
Bowlby suggested that a safe and strong environment is important for a child’s overall growth. Ainsworth suggested that there are secure and insecure attachments. While secure attachment fosters trust and comfort with intimacy, insecure attachment styles may lead to difficulties in forming and maintaining healthy relationships [3].
Understanding attachment styles can help us overcome our personal challenges and build empathy and compassion for people around us.
More Information about Dealing with Mommy Issues in Relationship
Types of Attachment Styles
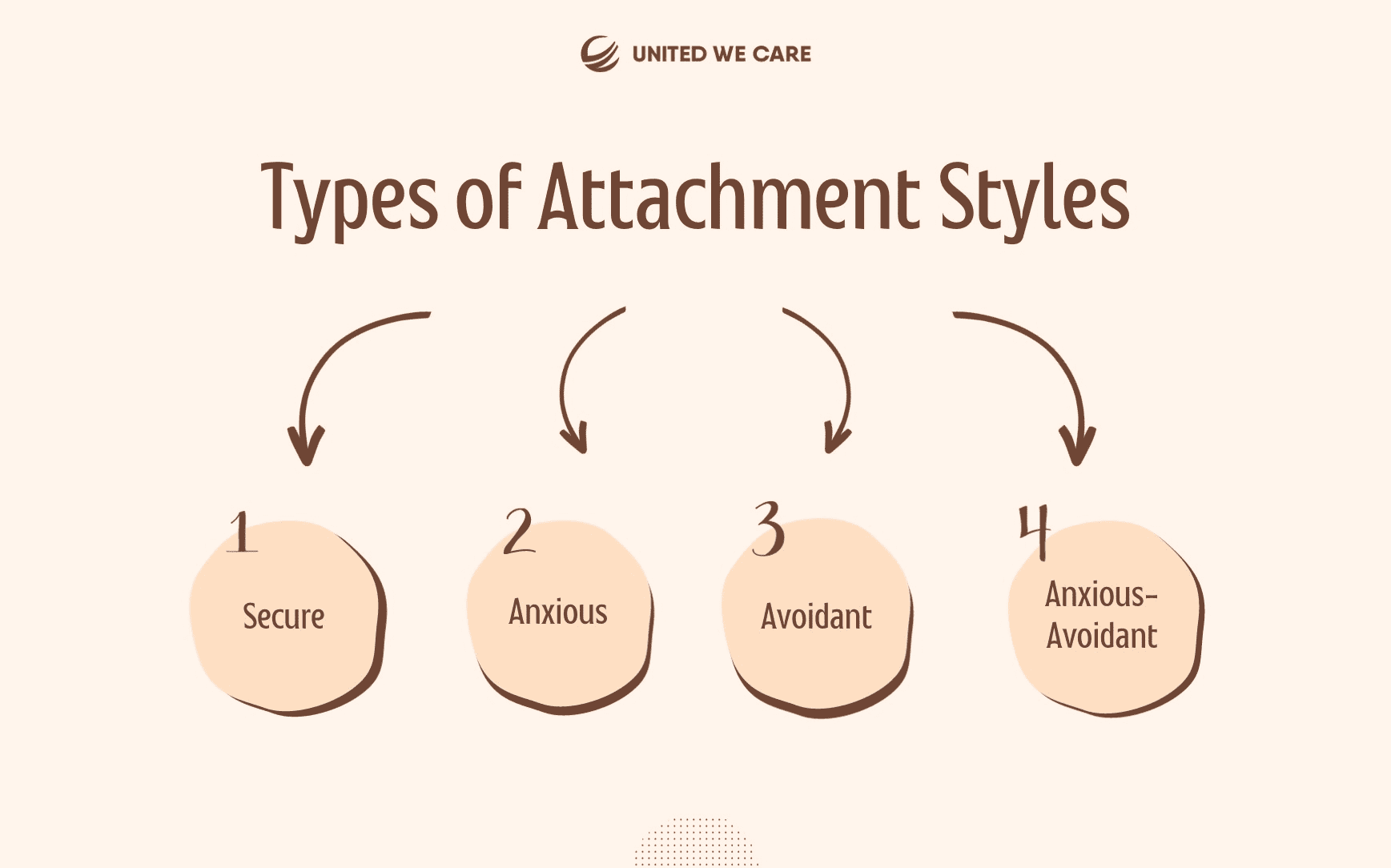
Bowlby and Ainsworth suggested for types of attachment styles [4]:
- Secure Attachment: If you are someone with a secure attachment style, you probably had a beautiful relationship with your caregivers, who showed love at the right places but also taught you lessons at the right places. You will have a positive outlook about yourself and the people around you. Emotional connections don’t scare you, which makes trusting and depending on your partner quite easy. Such a relationship helps give space for each other to grow in the relationship and as individuals.
- Anxious Attachment: If you have an anxious attachment style, it is possible that your caregiver was available sometimes and ignored you other times. If this behavior sounds familiar, then it’s likely that you look for love and emotional validation from your partner and people around you. You might even be emotionally dependent on your partner. The biggest trait of people with an anxious attachment is the fear of abandonment- you might worry that everyone will leave you eventually.
- Avoidant Attachment: As someone with an avoidant attachment style, you are likely to be independent and self-reliant. However, that also means that you run away from intimacy and emotional connections because doing that makes you feel uncomfortable. This behavior might be a result of your childhood, as your caregivers were absolutely emotionally distant and disregarding you. You might also find it difficult to trust and rely on others.
- Anxious-Avoidant Attachment: If you are a combination of both anxious and avoidant attachment styles, then this is the category you belong to. The reason behind such an attachment style can be a traumatic event and the caregiver’s inconsistent attitude. As someone with an anxious-avoidant attachment, you might have two minds about your relationships. It is possible that you might want emotional bonding but also have a fear of rejection and getting hurt. Your conflicting thoughts and emotions might lead to you seeking intimacy but also pushing people away.
More information about-What causes mommy Issues in women
Impact of Attachment Styles on Children
Attachment styles impact a child emotionally, socially, and in terms of mental development [5]:
- Regulating Emotions: Children with a secure attachment style are good at regulating their emotions well. Their caregivers provide them with safe and support to explore the world. They are confident and know that whenever needed, they can come to their caregivers. Children with an insecure attachment style, on the other hand, struggle with emotional management, leading to difficulties in coping with stress and anxiety.
- Social Skills: A secure attachment style leads to children having better social skills and care for others. They had positive experiences growing up with their caregivers. They are great at making and maintaining friendships due to how they saw their caregiver maintain their relationships. Children who are attached insecurely may face challenges relating to people around them, displaying clinginess, or withdrawing from socializing.
- Understanding the World: Children who grow up in a secure attachment style love to explore the world. This exploration leads to them engaging in curiosity-driven activities. This exploration leads to enhanced learning and problem-solving skills. Insecure attachment, in contrast, leads to children being too occupied with emotional issues, concentration, and focus.
- Self-Esteem: Growing up in secure environments, children have higher levels of self-esteem and self-worth. Insecure attachment is absolutely the opposite, and such children build their lives on negative beliefs.
Impact of Attachment Styles on Adults
Attachment styles largely influence us even in adulthood [6]:
- Romantic Relationships: Secure attachment leads to healthier and more satisfying romantic relationships. There is trust, communication, and emotional support. Insecure attachment: Contrarily, adults with insecure attachment styles may have intimacy issues, be jealous, and face challenges in maintaining stable relationships.
- Managing Emotions: Securely attached adults are able to manage stress and emotions better than insecurely attached adults. They are ready to seek help and comfort, but insecurely attached adults have difficulty expressing their needs and avoid emotional connections.
- Parenting: Parents exhibit the same behaviors and relationships to their children that they grew up with. Parents with secure Attachment styles are responsive and caring toward their children, whereas parents with insecure attachment styles show emotional highs and lows, cannot set boundaries, and are inconsistent.
- Parenting and Friendships: Secure attachments lead to wonderful friendships. They are loving and long-lasting. As parents, too, they impart the same feelings to their children. Insecure attachments, on the other hand, have difficulty trusting people and have friendships that don’t last too long. As parents, they are not around their children much or don’t always show love.
- Mental Health: Adults with secure attachments are resilient and have lower stress and anxiety levels. Insecurely attached adults can struggle with stress, depression, and high-functioning anxiety.
Read more about Anxious attachment.
Strategies to Overcome the Adverse Effects of Insecure Attachment Styles
You don’t have to be a victim of your past. Overcoming the adverse effects of insecure attachment styles requires self-awareness and breaking the cycle [7]:
- Become Self-Aware: Becoming aware of your patterns can help you break the patterns. One great way to do that is by writing journals. Another practice you can follow is mindfulness. It can even help you manage emotions.
- Seek Professional Help: A trained therapist can help you find the root cause of attachment-related issues and challenge negative beliefs. They can even teach you certain coping techniques.
- Social Support: Having supportive, loving, and caring people around you can help break the patterns. Such people can make you experience a world that is safe and beautiful and help you grow as an individual.
- Set Boundaries: You need to learn to say no and set boundaries so that you don’t cause further hurt and harm to yourself.
More Information about Mommy Issues Vs. Daddy Issues
Conclusion
Attachment styles get formed in childhood, and their effects can be seen in adulthood as well. There are four styles of attachment- secure, anxious, avoidant, and anxious-avoidant. Securely attached people are trusting, comfortable with intimacy, and independent. Anxious attachment leads to fear of abandonment and emotional dependency. Avoidant individuals may avoid closeness to maintain independence, while anxious-avoidant individuals are always conflicted about their emotions. These attachment styles impact what kind of relationships they have with themselves and others.
To know more, you can reach out to our expert counselors or explore more content at United We Care! At United We Care, a team of wellness and mental health experts will guide you with the best methods for well-being.
References
[1]“Attachment Quotes (509 quotes).” https://www.goodreads.com/quotes/tag/attachment
[2] K. C. MSEd, “What Is Attachment Theory?,” Verywell Mind, Feb. 22, 2023. https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-attachment-theory-2795337
[3] S. Mcleod, “Attachment Theory: Bowlby and Ainsworth’s Theory Explained,” Simply Psychology, Jun. 11, 2023. https://www.simplypsychology.org/attachment.html#:~:text=Attachment%20styles%20refer%20to%20the,how%20you%20parent%20your%20children.
[4] M. Mandriota, “Here Is How to Identify Your Attachment Style,” Psych Central, Oct. 13, 2021. https://psychcentral.com/health/4-attachment-styles-in-relationships#whats-next
[5] C. E. Ackerman, “What is Attachment Theory? Bowlby’s 4 Stages Explained,” PositivePsychology.com, Apr. 19, 2023. https://positivepsychology.com/attachment-theory/
[6] Team, “Attachment Styles and Their Role in Adult Relationships,” Attachment Project, Apr. 06, 2023. https://www.attachmentproject.com/blog/four-attachment-styles/#:~:text=There%20are%20four%20adult%20attachment,Secure
[7] M. F. L. Lmft, “Coping With an Insecure Attachment Style,” Verywell Mind, Dec. 05, 2022. https://www.verywellmind.com/marriage-insecure-attachment-style-2303303#toc-overcoming-an-insecure-attachment-style